Ten things the Romans didn’t want you to know about the Etruscans
The Etruscans get a bad rap. When the Greeks and Romans wrote the history of their time they intentionally left the Etruscans out. In the case of Rome, the victors get to write history. The result is that even my daughter, Donella, has a disdain for the Etruscans after spending five years in the Italian school system.
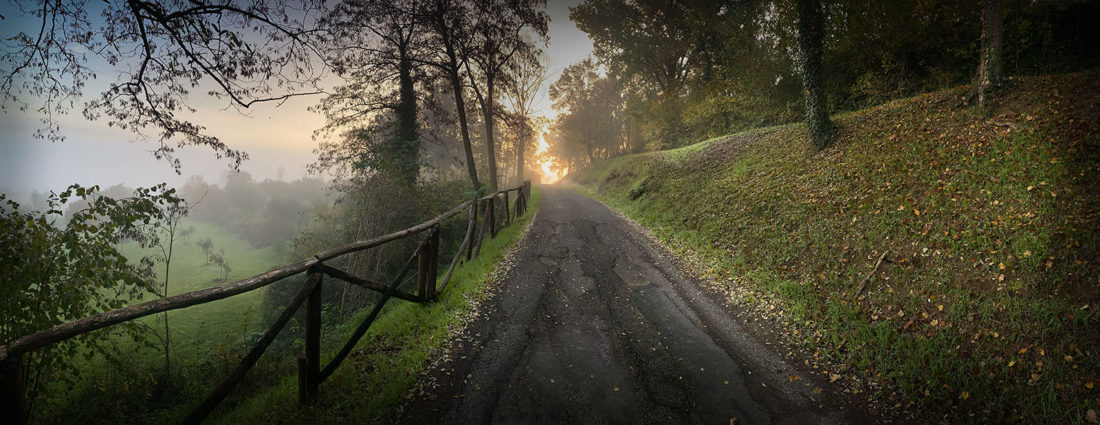
We live on an Etruscan road (the little lane above) and it’s made me curious to know more, as does living with the Tuscans and noting how different they are from the people of other regions—where did this difference come from? I’ve been investigating and here are ten reasons that I’m intrigued by this ancient civilization. (The Etruscans lived from 900 BCE to 89 BCE in present day Tuscany (and far beyond), and gave the region their name.)
1. Women were equals. Woman were literate and some were noteworthy scholars, they participated freely in the public sphere, became judges, dressed in any way they chose, and participated in banquets as equals to men and could drink, dance, and lounge on couches. The contemporary Greeks and Romans thought these women’s rights were scandalous. They kept their own names when marrying and people buried in Etruscan tombs were identified by their mother and father’s lineage. Women in art were represented with their heads on the same level as men, and as having the same torso size, which is clearly a physical exaggeration, but conveyed equality. When the Romans dominated the Etruscan culture women lost all these rights.
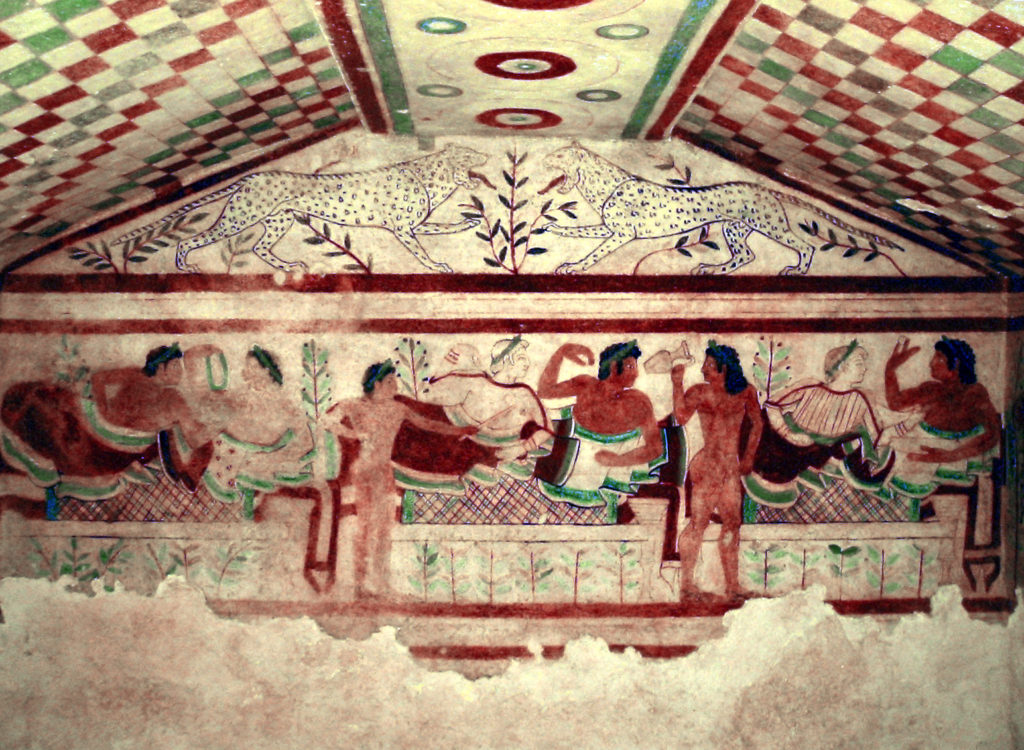
I visited the tombs at the Necropolis in Tarquinia (and took a private 2.5 hour tour) and in the Tomb of the Leopards (480-450 BCE) three couples are shown at a banquet. The pair on the right especially grabbed my attention. I think it is one of the most beautiful images I’ve ever seen of a couple’s relationship. There is such energy, enjoyment, and engagement in their body language.

2. They chose equal city-states over centralized power. The civilization was a federation of twelve equally-powerful cities. Key to Etruscan success was the idea that it was better to specialize, cooperate, and trade rather than fight amongst themselves for power. This made them very successful and wealthy. Cities specialized in different things, like mining and metal work, ceramics, food production, or cloth production. This specialization let technology surge ahead, which increased food production, which let more people specialize. A virtuous cycle.
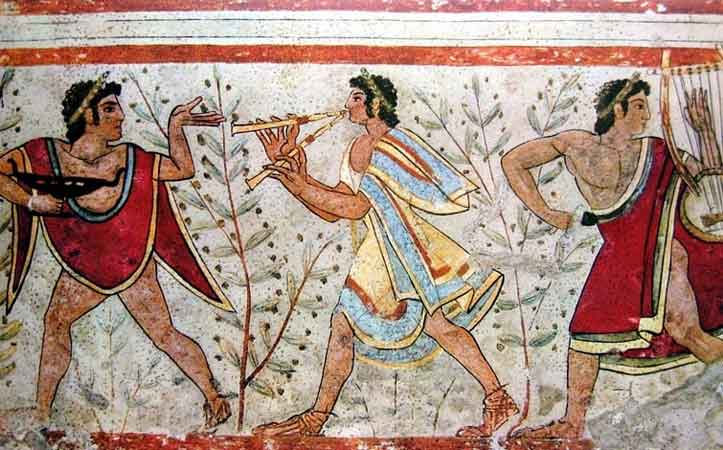
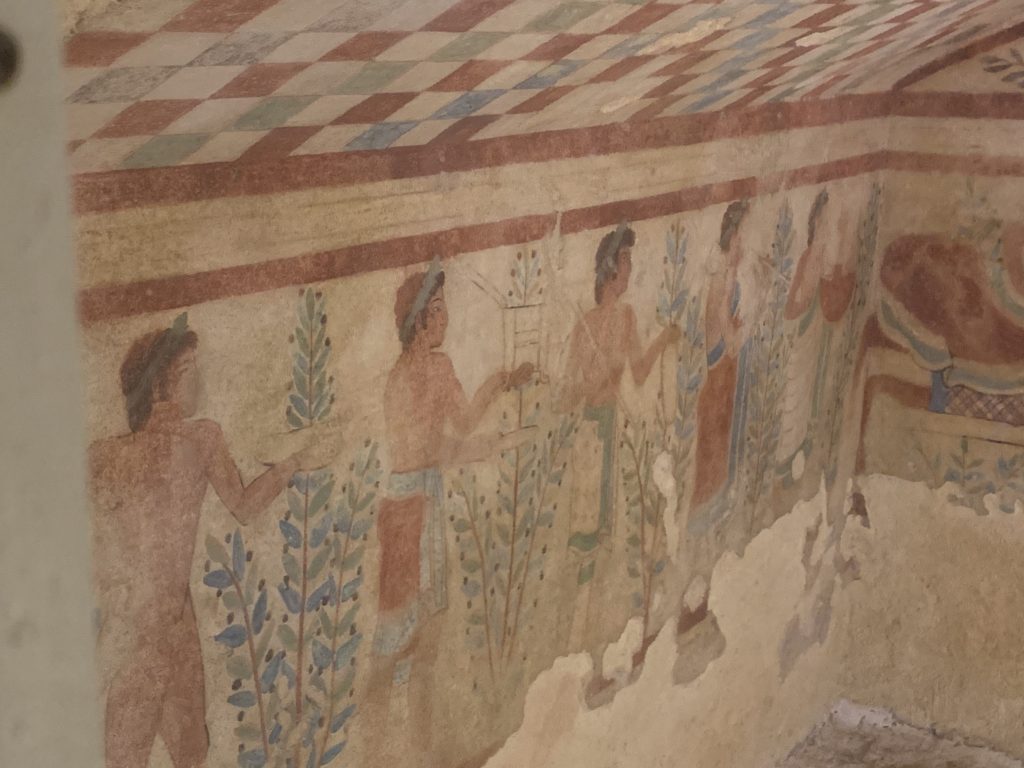
3. The fashion was amazing. For several centuries when the Romans wanted to say someone was really stylish they’d say someone dressed like an Etruscan. In the painting above the women are wearing three different patterns of cloth: stripes, polka dots, and stars. And check out the center musician from the same tomb as he walks through a field of olives with two other band members. His clothes are amazing, billowing backwards as he walks forward. And his shoes are marvelous. The Italian gift for designing clothes and shoes started early.

Etruscan jewelry is also beautiful. I love the things that started with the Etruscans and endure today. The town of Arezzo remains one of the top places in the world for gold processing and design, and its Etruscan predecessor was famous for metal work, including jewelry. Look at these Etruscan bracelets.

4. Italy with no olive oil or wine? The Etruscans brought the cultivation of grapes for wine and olives for oil to Italy from their contacts with the Greeks at the end of the third century BCE.
5. Romans would not have been the Romans without them. The Etruscans predated the Romans and then were subsumed by the Roman Empire in 89 BCE when the Romans stamped out their rights, culture, and language. The Etruscans got the alphabet and numbers from the Phoenicians and passed them on to Rome. The Etruscans also taught the Romans hydraulic engineering, city planning with streets in a grid, fashion (including the toga), architecture (temple design and the Etruscan adaptation of Doric columns) and more. Two of the last Roman kings were Etruscan. The most famous statue of Romulus and Remus and the she-wolf—the symbol of Rome—was created by an Etruscan.
6. They were the creators of the red-checkered table cloth. Some Italian traditions run deep. Check out what the lounging couples are sitting on in the painted scene above.
7. These guys got around. I am always amazed when I learn the extent of trade relationships that existed thousands of years ago. The Etruscans were one of the major players. They traded with Greece, Turkey, Egypt, the Phoenicians, and even the Celts.
8. Social mobility was celebrated. Although they did have slaves, apparently freedmen and women had many opportunities to cross occupations and social classes. One third of the paintings in the Tomb of the Leopards is about this topic. The same figure is repeated four times, starting on on the left as a naked slave and ending up on the right as a well-dressed member of society coming to the banquet.

9. They had great taste. More revered Greek attic vases, or kraters, have been found in Etruscan tombs than anywhere else, including one of the most infamous pieces of art the Metropolitan Museum of Art in New York has ever had, the Sarpedon Krater. This piece of pottery was looted from an Etruscan grave in 1971 and the Met illegally bought it a year later for the most they’d ever paid for a piece of art. The Krater was repatriated to Italy and moved from its centerpiece position in a Tiffany-designed case to a more humble Italian museum very near where it had been found.
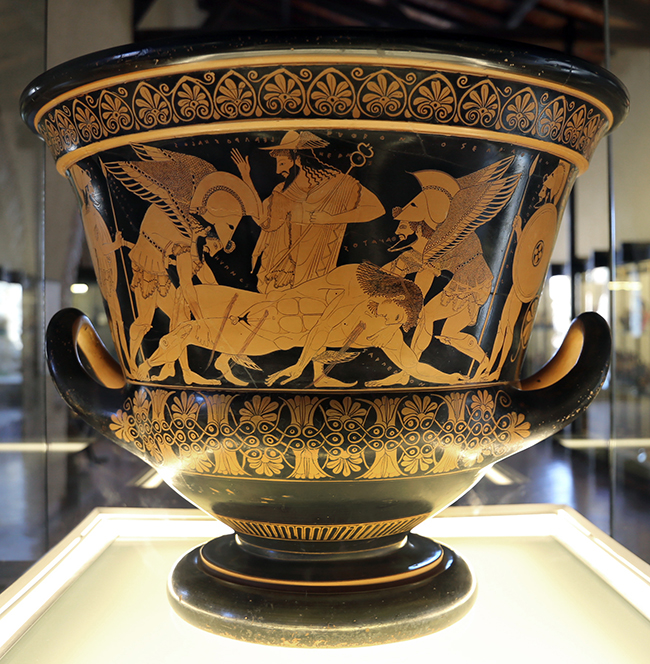

The Etruscans also made Kraters that have been found in Greek tombs.
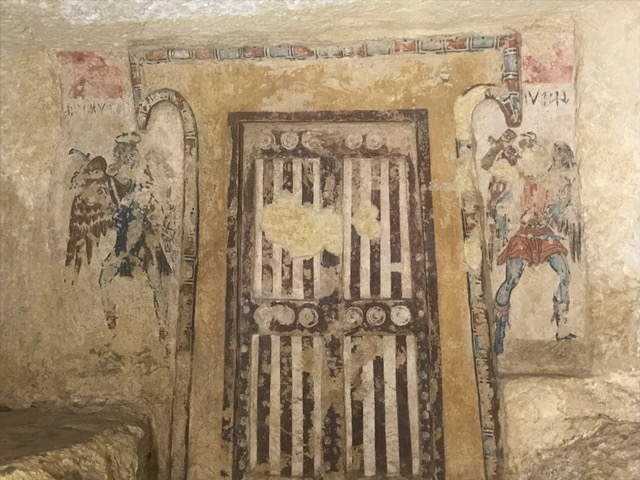
10. Precocious artists. The fresco is badly damaged, but look at the nuanced leg muscles on the guy on the right (and the shoes!). Predates the rediscovery of perspective and portrayal of anatomy in the Renaissance by 1400 years. And the door to the underworld actually has plaster relief working with the painting to amplify a 3-D effect.

If you are still with me in my rabbit hole I applaud you. If you want more I found this, this, and this helpful as good overviews of the Etruscan civilization.